Binary Tree Algorithms
Common binary tree algorithms from leetcode.
Operations
API for Binary Tree Node.
1 | public class TreeNode { |
Tree Traversal
Traversing(遍历) a tree means visiting and outputting the value of each node in a particular order.
There're typically 3 ways of tree traversal:
Inorder(中序遍历) => Left, Root, Right.
Preorder(前序遍历) => Root, Left, Right.
Post order(后序遍历) => Left, Right, Root.
E.g.:
1 | 1 |
- Preorder: 1, 2, 4, 5, 3
- Inorder: 4, 2, 5, 1, 3
- Postorder: 4, 5, 2, 3, 1
Construct Binary Tree from Traversal
105. Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal
106. Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal
可以通过 (中序,前序) 或 (中序,后序) 遍历来构造二叉树.
1 | int[] preorder;//前序遍历结果, 由三部分组成: (root, root.left, root.right) |
以 (中序,前序) 为例:
1 | public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) { |
由于
preorder[]第一个就是根节点的值.通过在inorder[]中寻找该值, 就可以找到root节点, 并且找到root的左右子树.1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8// root 节点对应的值就是前序遍历数组的第一个元素
int rootValue = preorder[preStart];
// rootValue 在中序遍历数组中的索引
int rootIdxForInorder = map.get(rootValue);
int leftSize = rootIdxForInorder - inStart;
int rightSize = inEnd - rootIdxForInorder - 1;对左右子树再递归地进行构造, 即可得到完整的二叉树. (中序,后序) 也同理.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7// 先构造出当前根节点
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootValue);
// 递归构造左右子树
root.left = buildBinaryTree(preorder,preStart+1, preStart+leftSize+1, inorder, inStart, inStart+leftSize, map );
root.right = buildBinaryTree(preorder,preStart+leftSize+1, preEnd, inorder, inStart+leftSize+1, inEnd, map );
return root;
- 无法通过 (前序,后序) 遍历来构造二叉树, 因为在知道root节点后无法得到其左右子树.
Example
E.g.:
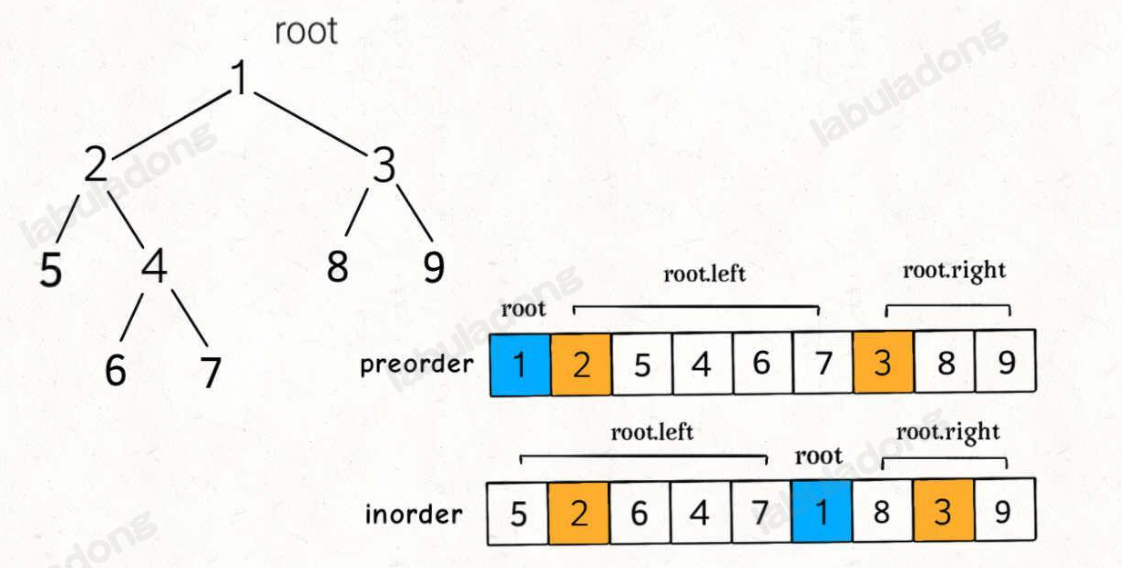
如图所示, 从preorder[0]得到root节点的值为1, 使用此信息从indorder[]中查找到root节点.
接下去得到root左右子树的preorder和inorder[]:
- root.left:
preorder[]={2,5,4,6,7}inorder[]={5,2,6,4,7}
- root.right:
preorder[]={3,8,9}inorder[]={8,3,9}
对左右子树再按照上述步骤递归即可.
Get Depth
111. Minimum Depth of Binary Tree